Digital Learning Plan: Origins and Rationale
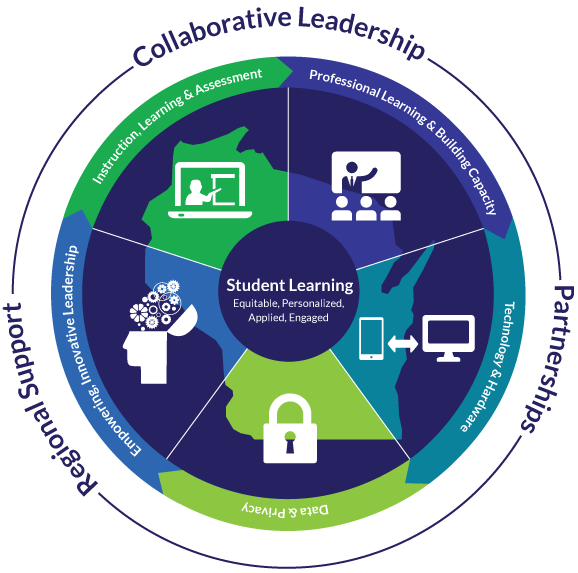
The State Superintendent’s Digital Learning Advisory Council (DLAC) established a shared vision for digital learning in Wisconsin. The DLAC was created in 2011 to provide intellectual and practical insights into all aspects of digital learning in Wisconsin. The DLAC was charged with developing a comprehensive plan for PK-12 digital learning in Wisconsin. The DLAC adopted the Future Ready Framework as a way to organize our key priorities and planning tools for districts. That vision called for equitable, personalized, applied, and engaged digital learning for all students. As Wisconsin school districts begin to implement this vision, they are encouraged to consider the following areas: instruction, learning, and assessment; empowering, innovative leadership; technology & hardware; professional learning and building capacity; and data and privacy. School districts in Wisconsin do not make this journey in isolation. Existing statewide systems are in place, and our colleagues nationwide have provided invaluable support and resources.
The skillful and equitable use of technology can transform the way teaching and learning happen in classrooms across Wisconsin. Digital tools can enhance student learning as they connect efforts to identify what students should know and be able to do as well as help students and educators assess progress toward achieving academic goals. To meet the needs of today's students and to ensure they are college and career ready, schools are encouraged to be innovative in providing student learning experiences, adopting technologies and instruction in ways, which meaningfully engage the digital generation. As a result, students will have equitable opportunities to have teachers who are trained to provide those digital opportunities that promote critical thinking, communication, collaboration, and creativity and innovation.
Need and Goals for the Wisconsin Digital Learning Plan
The 2012 Wisconsin Digital Learning Plan served as the foundation for the 2016 Wisconsin Digital Learning Plan. This updated Plan is a roadmap to follow for schools and their partners including stakeholders, community organizations, and local employers. The Plan provides school districts strategies for making learning more meaningful and relevant for students, more accessible for economically disadvantaged students, and more cost-effective upon implementation. The focus, throughout the Plan, continues to be learning environments that are equitable, personalized, applied, and engaging.
Equitable Access
Recommendations in all areas focus on providing equitable access to technology for all students, learners, and educators across the state. This includes Internet connection speeds and infrastructure support that allow learning to occur anywhere and anytime. Access to high-quality digital resources, virtual instruction, and technology-enhanced learning—supported and aligned with Wisconsin’s academic standards—must be ubiquitous.
Personalized Learning
The learner experience must be personalized using technology so learning is engaging and relevant, with the goal of maximizing each person’s learning potential. Technology must be leveraged to directly account for the voice of the learner, whether student or teacher, in instruction. Recommendations regarding infrastructure, professional development, curriculum, assessment, and leadership promote these dynamic and flexible learning formats.
Applied and Engaging Learning
Critical skills such as problem-solving, creativity and innovation, communication, and collaboration are central to being career and college ready. Driven by a desire to raise achievement and learning for all Wisconsin students to world-class levels in mathematics, science, technology, and English language arts, students must communicate and collaborate effectively, do research, think critically and creatively, and solve problems that address the future needs of our global society, anywhere and anytime. Students must be prepared with the knowledge and the ability to apply these critical skills to succeed in college and careers.
While formal technology plans are no longer required by state or federal statutes, it is strongly recommended that districts use the 2016 Wisconsin Digital Learning Plan as a planning guide to achieving short and long-term digital learning goals. Districts are encouraged to integrate digital learning planning into their district strategic and continuous improvement planning processes. The Plan’s alignment with federal and state laws, policies, and initiatives makes it a valuable resource as districts implement the components of the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA).
Definition of Digital Learning
The Alliance for Excellent Education defines digital learning as “any instructional practice that is effectively using technology to strengthen the student learning experience. Digital learning encompasses a wide spectrum of tools and practices, including;
- online and formative assessments
- increased focus and quality of teaching resources
- reevaluating the use of time
- online content and courses
- applications of technology in classrooms and school buildings
- adaptive software for students with special needs
- learning platforms
- participation in professional communities of practice
- access to high-level and challenging content and instruction
- and many other advancements technology provides to teaching and learning.”
Throughout this plan, you will see references to the Future Ready Interactive Planning Dashboard created by the Alliance for Excellent Education. This Dashboard assists districts as they assess, plan, implement, and revise their own district digital learning plans and district strategic plans.
In the article, “9 Steps to a Future-Ready Education,” the author suggests these nine steps to consider in order to bring future-ready momentum to the classroom:
- Embrace a powerful vision of student-led learning.
- Align leadership management, and resources with goals.
- Assess where your schools are now.
- Identify the future-ready skills to focus on.
- Create a professional development plan for future-ready skills.
- Grant students equitable access to technology and information.
- Develop assessments to measure student progress in future-ready skills.
- Collaborate with outside partners and community.
- Plan collectively and strategically for the future.
Wisconsin has adopted five of the Future Ready Framework Gears: Instruction, Learning, and Assessment; Technology and Hardware; Empowering, Innovation Leadership; Professional Learning and Building Capacity; and Data and Privacy. Common to these initiatives are: equitable access to technology and connectivity inside and outside of school, regardless of students’ backgrounds; a comprehensive learning infrastructure including digital learning content and other resources; professional development for educators and education leaders, which moves them from a conventional teaching and learning classroom to a guided online environment; and establishment of a robust technology infrastructure meeting current connectivity goals and can be augmented to meet future demand.
Process and Outreach in Developing this Plan
Many resources and reference points were used by the DLAC that created this updated Wisconsin Digital Learning Plan. During the update process, the United States Department of Education released the 2016 National Education Technology Plan, which provides the following insights used in developing the Plan:
- A digital-use divide continues to exist between learners who are using technology in active, creative ways to support their learning and those who predominantly use technology for passive content consumption.
- Research on the effectiveness of technology-enabled programs and resources is still limited, and we should build the capacity to generate evidence of individuals, programs, and community-level outcomes.
- Many schools do not yet have access to or are not yet using technology in ways that can improve learning on a daily basis, which underscores the need—guided by new research—to accelerate and scale up adoption of effective approaches and technologies.
- Few schools have adopted approaches for using technology to support informal learning experiences aligned with formal learning goals.
- Supporting learners in using technology for out-of-school learning experiences is often a missed opportunity.
- Across the board, teacher preparation and professional development programs fail to prepare teachers to use technology in effective ways.
- Assessment approaches have evolved but still do not use technology to its full potential to measure a broader range of desired educational outcomes, especially non-cognitive competencies.
- The focus on providing Internet access and devices for learners should not overshadow the importance of preparing teachers to teach effectively with technology and to select engaging and relevant digital learning content.
- As students use technology to support their learning, schools are faced with a growing need to protect student privacy continuously while allowing the appropriate use of data to personalize learning, advance research, and visualize student progress for families and teachers.
Another critical touch point used in the development of the 2016 Wisconsin Digital Learning Plan is the recently re-authorized Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA). As school districts plan for the implementation of the ESSA, the role of digital literacy programming to provide instructional supports is more prominent than ever before. Every section of ESSA makes some reference to the role of technology as it relates to student and professional learning.
To assist in the development of the Plan, DPI and DLAC collaborated with other states, regional, and national agencies on initiatives to ensure the new Digital Learning Plan was cohesive and inclusive. Some of the collaborators include: the Cooperative Education Service Agencies (CESAs) in Wisconsin, the Wisconsin Technology Leaders Association (WETL), Consortium for School Networking (CoSN), Wisconsin Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (WASCD), State Educational Directors of Technology Association (SEDTA), Wisconsin Association of School District Administrators (WASDA), Wisconsin Association of School Boards (WASB), Wisconsin Educational Media and Technology Association (WEMTA), and the Wisconsin Association of School Business Officials (WASBO).
Plan Format and Uses of the Plan
All sections of the 2016 Wisconsin Digital Learning Plan align with the Future Ready Framework as well as the National Education Technology Plan. The Plan is a roadmap for the DPI to use in making strategic decisions regarding agency resource allocation and implementation. This Plan also serves as a roadmap for districts when developing their local digital learning plan for funding allocations, professional development, infrastructure planning, and instructional practices. The Plan also focuses on topics outlined in the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA).
Each of the gears of the 2016 Wisconsin Digital Learning Plan includes the following: planning questions to consider, goals and recommendations followed by priority activities, and resources. At the end is a glossary of terms commonly found in any discussion about digital learning today. The resource lists and glossary are starting points for reference information - new blogs, papers, books, and other resources emerge almost daily to assist us in this journey. The DPI website has a wealth of resources and many are linked in this document.
The Plan Goals, Recommendations, and Priority Activities within each gear represent issues which speak to our engagement with federal, state, and local education agencies. Activities are targeted for completion by the state education agency (SEA) and local education agency (LEA). In many cases, there will be a collaboration between and among agencies to meet the goals.
The 2016 Wisconsin Digital Learning Plan is about teaching and learning in the digital environment in which citizens now live and work and not about devices, software, apps, or the latest tools. The Plan encourages thoughtful planning, preparation, and analysis of student outcomes, professional learning, culture, and leadership. Most importantly, the Plan is about meeting our vision of equitable, personalized, applied, and engaged digital learning for all students.
Note: Alliance for Excellent Education, Future Ready Framework and US Department of Education, National Ed Tech Plan. Used with Permission.