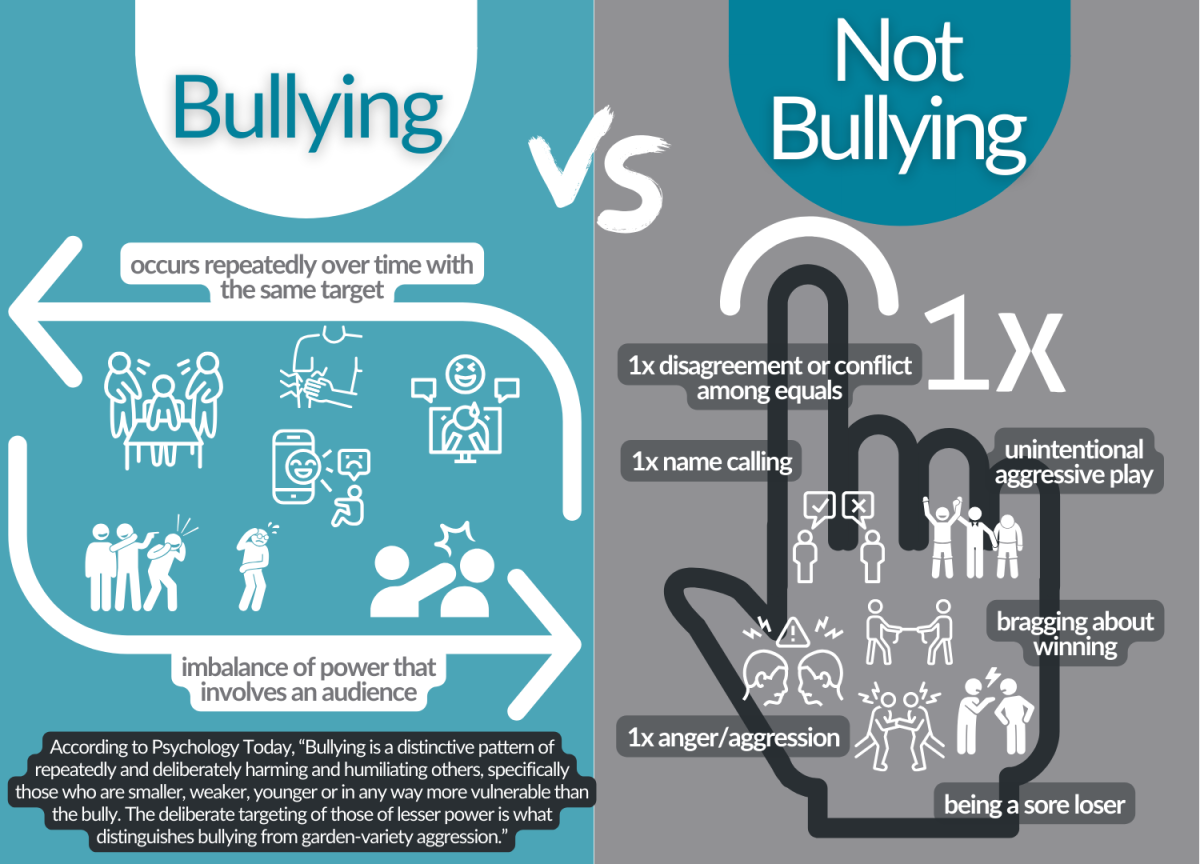
According to the Pew Research Center, "Nearly half of U.S. teens have been bullied or harassed online, with physical appearance being seen as a relatively common reason why. Older teen girls are especially likely to report being targeted by online abuse overall and because of their appearance."
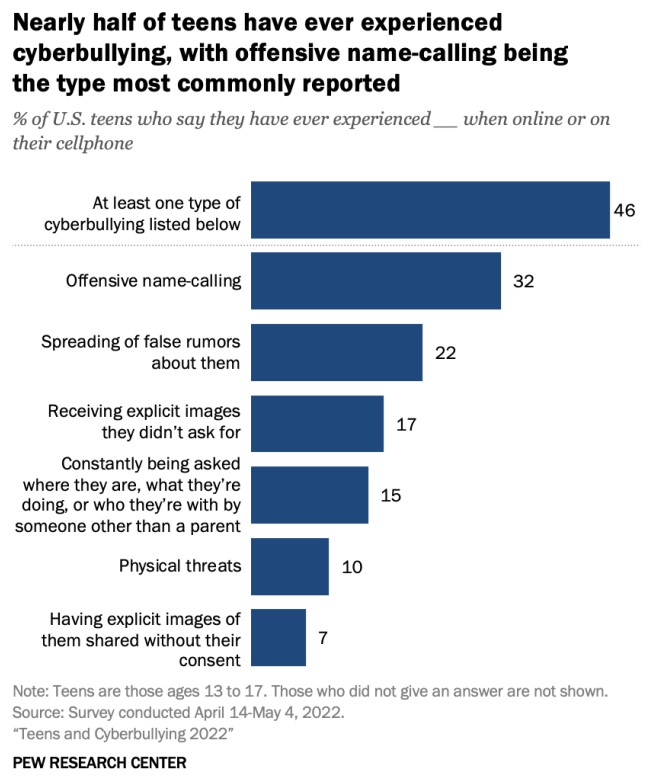
According to the Cyberbullying Research Center in 2020, "Almost 15% of tweens have seen cyberbullying, and nearly as many have been targeted. Six percent of tweens have been cyberbullied many times, while another 8.5% were cyberbullied once or twice. Few tweens admit to cyberbullying others (3.2%).
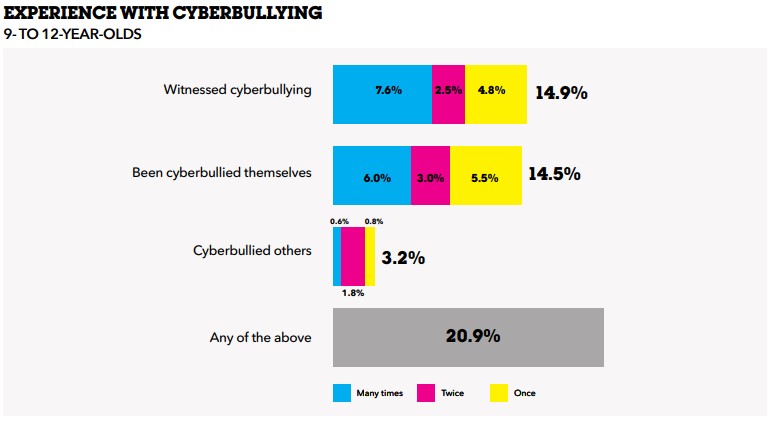
What constitutes bullying?
It is important to distinguish between bullying and other forms of negative behavior to address them appropriately. Bullying is harmful and requires intervention to protect the well-being of those involved, while other conflicts or disagreements may be resolved through communication and conflict resolution strategies. Bullying is a pattern of repeated aggressive behavior, involving a power imbalance, that is intended to harm or intimidate another individual or group. Genuine conflicts or disagreements between individuals that involve mutual respect and a lack of intent to harm do not qualify as bullying. Healthy conflict resolution aims to find a solution rather than perpetuate harm. Isolated incidents of negative behavior or conflicts do not constitute bullying, as bullying involves a pattern of repeated behavior aimed at the same target. In addition, interactions between peers, even if they involve disagreements or arguments, may not be classified as bullying unless they involve a power imbalance and repeated malicious intent to harm. Bullying of any kind is a serious matter and should be dealt with swiftly and firmly. However, before labeling something as bullying, be certain to get the facts about the incident(s) and/or behavior(s) before rushing to judgement.